Art-ranking activity: the ovarian cycle – Embark on an exploration of the fascinating interplay between art-ranking activity and the intricate hormonal fluctuations of the ovarian cycle. This investigation unveils the profound impact of physiological, cognitive, emotional, and cultural factors on our aesthetic preferences, revealing the multifaceted nature of human perception.
As we delve deeper into the subject, we will examine the hormonal changes that orchestrate the ovarian cycle, their influence on brain function, and the potential implications for art-ranking activity. We will also explore the cognitive processes that underpin art ranking, such as attention, memory, and decision-making, and how the ovarian cycle may modulate these mechanisms.
Physiological Foundation of Art-Ranking Activity
The ovarian cycle, a series of hormonal changes that occur in women, has been linked to fluctuations in brain function and behavior. These hormonal changes may influence art-ranking activity, the process of evaluating and ranking artwork.
Hormonal Changes During the Ovarian Cycle
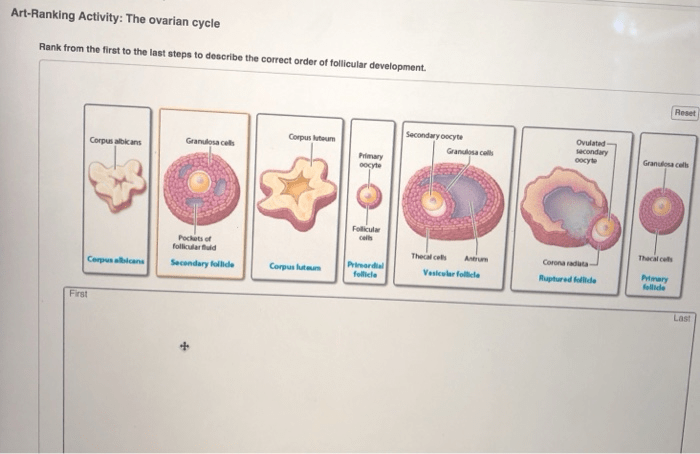
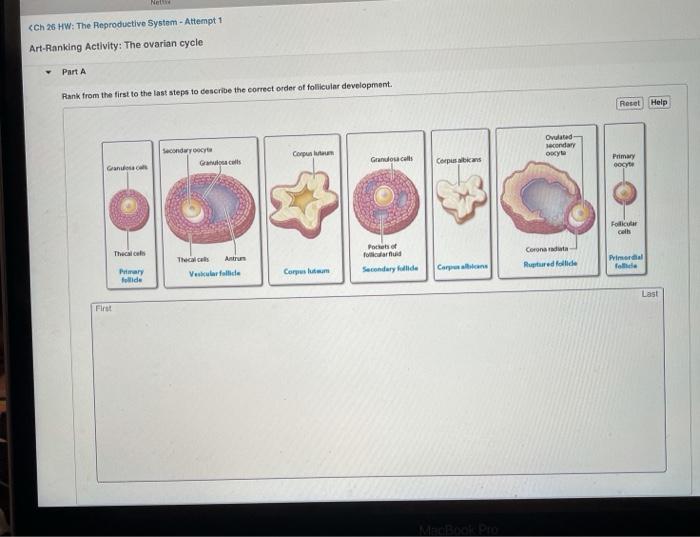
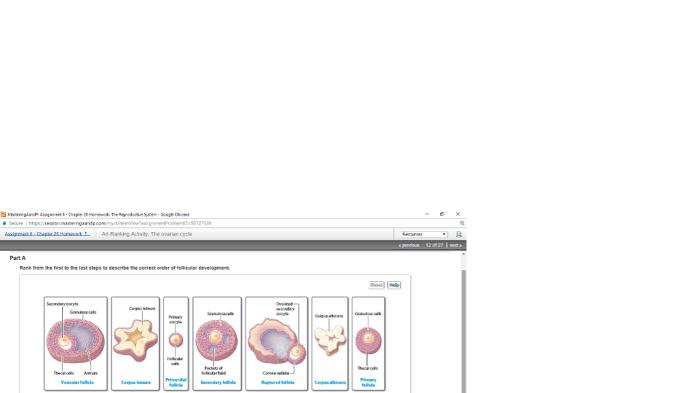
The ovarian cycle consists of four phases: the menstrual phase, follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase. Each phase is characterized by specific hormonal changes:
- Menstrual phase:Estrogen and progesterone levels are low.
- Follicular phase:Estrogen levels rise, stimulating the development of a follicle in the ovary.
- Ovulation:A surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers the release of an egg from the ovary.
- Luteal phase:Progesterone levels rise, preparing the uterus for possible pregnancy.
Impact of Hormonal Changes on Brain Function
These hormonal changes have been shown to affect brain regions involved in cognitive processes, such as attention, memory, and decision-making.
Influence on Art-Ranking Activity
The hormonal fluctuations during the ovarian cycle may influence art-ranking activity in the following ways:
- Enhanced attention:Estrogen has been linked to improved attention, which may enhance the ability to focus on and appreciate artwork.
- Improved memory:Progesterone has been associated with enhanced memory, which may facilitate the recall and recognition of artwork details.
- Altered decision-making:The hormonal changes during the ovarian cycle may influence risk-taking and reward-seeking behavior, which could impact the evaluation of artwork.
Cognitive Mechanisms Underlying Art-Ranking Activity
Cognitive Processes Involved
Art-ranking activity involves several cognitive processes, including:
- Attention:Focusing on specific aspects of the artwork.
- Memory:Recalling and recognizing details about the artwork.
- Decision-making:Evaluating and ranking the artwork based on personal preferences.
Ovarian Cycle Modulation
The ovarian cycle may modulate these cognitive mechanisms by influencing:
- Attention:Estrogen may enhance attention to detail, while progesterone may promote a broader focus.
- Memory:Progesterone may improve memory for specific details, while estrogen may facilitate the recall of general impressions.
- Decision-making:The hormonal changes during the ovarian cycle may influence risk-taking and reward-seeking behavior, which could impact the decision-making process.
Emotional and Motivational Factors in Art-Ranking Activity
Influence of the Ovarian Cycle
The ovarian cycle can affect emotional and motivational factors that influence art-ranking activity, such as:
- Emotions:Estrogen has been linked to positive emotions, while progesterone may promote feelings of calmness.
- Motivations:The hormonal changes during the ovarian cycle may influence the desire to engage in art-ranking activities.
Impact on Art-Ranking Preferences
These emotional and motivational changes may impact art-ranking preferences in the following ways:
- Positive emotions:Estrogen-induced positive emotions may lead to a preference for artwork that evokes positive feelings.
- Calmness:Progesterone-induced calmness may promote a preference for artwork that provides a sense of tranquility.
- Motivation:Fluctuations in motivation during the ovarian cycle may influence the willingness to participate in art-ranking activities.
Cultural and Social Influences on Art-Ranking Activity
Cultural and Social Factors
Art-ranking activity is influenced by cultural and social factors, including:
- Cultural norms:Societal values and beliefs can shape art preferences.
- Social expectations:Peer influence and social media can impact art-ranking behavior.
Interaction with the Ovarian Cycle
The ovarian cycle may interact with these cultural and social factors in the following ways:
- Hormonal changes:The hormonal fluctuations during the ovarian cycle may influence the susceptibility to cultural norms and social expectations.
- Emotional state:The emotional changes associated with the ovarian cycle may affect the interpretation of social cues and interactions.
Impact on Art Preferences, Art-ranking activity: the ovarian cycle
The interplay between the ovarian cycle and cultural and social factors may influence art preferences in the following ways:
- Conformity:Hormonal changes during the ovarian cycle may influence the tendency to conform to cultural norms in art preferences.
- Individuality:Emotional changes may promote a desire for more personalized and unique art preferences.
Methodological Considerations for Studying Art-Ranking Activity
Research Study Design
To investigate the relationship between the ovarian cycle and art-ranking activity, a research study could be designed as follows:
- Participants:Women of reproductive age, organized into different phases of the ovarian cycle.
- Task:Standardized art-ranking task, where participants evaluate and rank artwork.
- Measurements:Art-ranking scores, hormonal levels, and other relevant variables.
Data Analysis
The data collected from the study can be analyzed using statistical methods to examine the relationship between the ovarian cycle and art-ranking activity.
Potential Applications of Research on Art-Ranking Activity
Art Therapy Interventions
Research on art-ranking activity can inform the development of personalized art therapy interventions:
- Tailored interventions:Understanding the influence of the ovarian cycle on art preferences can help therapists tailor interventions to specific phases of the cycle.
- Enhanced therapeutic outcomes:By incorporating art-ranking activities that align with hormonal changes, therapists may improve therapeutic outcomes.
Therapeutic Tool
Art-ranking activity can be used as a therapeutic tool in the following ways:
- Self-expression:Art-ranking can provide a means for individuals to express their emotions and experiences.
- Insight into preferences:By ranking artwork, individuals can gain insights into their personal preferences and values.
- Mood regulation:Art-ranking activities that evoke positive emotions may help regulate mood and promote well-being.
Top FAQs: Art-ranking Activity: The Ovarian Cycle
What is the significance of studying the relationship between art-ranking activity and the ovarian cycle?
This research offers valuable insights into the physiological, cognitive, and emotional factors that influence our aesthetic preferences. By understanding the role of the ovarian cycle in art-ranking activity, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of human perception and its implications for art therapy.
How can art-ranking activity be used as a therapeutic tool?
Art-ranking activity can be incorporated into art therapy interventions to facilitate self-expression, explore emotions, and promote self-awareness. By engaging with art in a structured and reflective manner, individuals can gain insights into their own preferences and the factors that shape them.