Delving into the realm of chemistry, the molecular formula and empirical formula worksheet serves as an invaluable tool for comprehending the composition of compounds. This worksheet empowers students to explore the intricacies of molecular and empirical formulas, unlocking a deeper understanding of their significance in chemical calculations and analysis.
This comprehensive worksheet provides a systematic approach to determining molecular and empirical formulas, guiding learners through the steps involved in these essential calculations. By engaging in hands-on activities, students will gain a practical grasp of the concepts and their applications in real-world scenarios.
1. Introduction to Molecular and Empirical Formulas
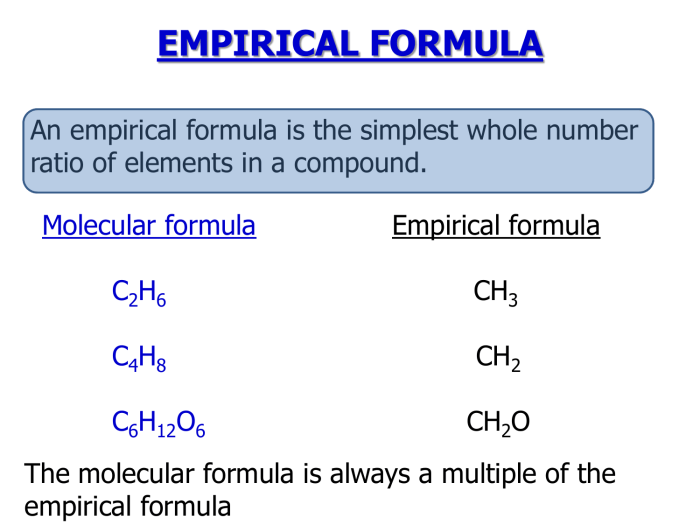
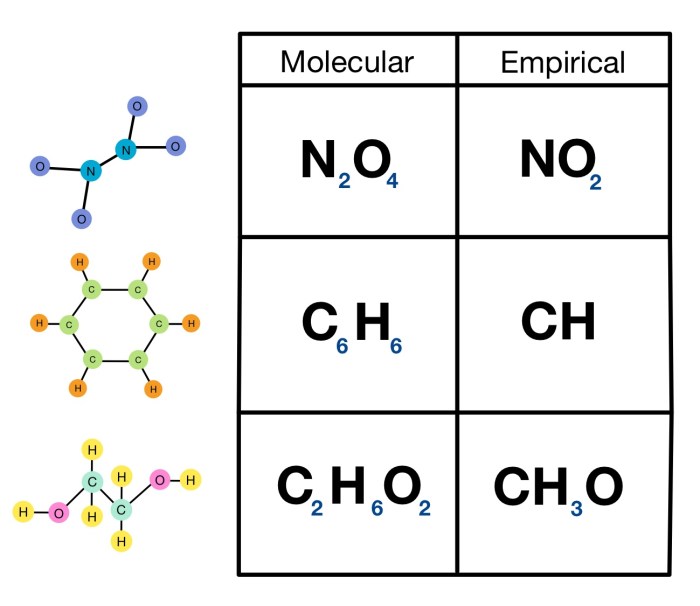
In chemistry, a molecular formula represents the exact number and types of atoms present in a molecule of a compound, while an empirical formula represents the simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in a compound.
The molecular formula provides detailed information about the molecular structure, whereas the empirical formula gives a basic understanding of the relative proportions of different elements in the compound.
Differences between Molecular and Empirical Formulas
- Molecular Formula:Provides the exact number of each type of atom in a molecule.
- Empirical Formula:Gives the simplest whole number ratio of atoms in a compound, not necessarily representing the actual molecular structure.
Examples of Molecular and Empirical Formulas, Molecular formula and empirical formula worksheet
- Molecular Formula of Glucose: C 6H 12O 6
- Empirical Formula of Glucose: CH 2O
2. Determining Molecular and Empirical Formulas: Molecular Formula And Empirical Formula Worksheet
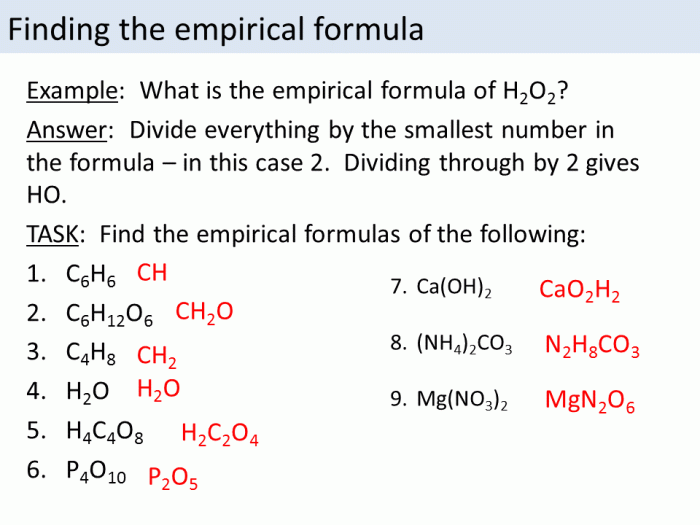
Determining the Molecular Formula
- Determine the empirical formula.
- Calculate the molar mass of the empirical formula.
- Divide the actual molar mass of the compound by the molar mass of the empirical formula.
- Multiply the subscripts in the empirical formula by the result obtained in step 3.
Determining the Empirical Formula
- Convert the mass of each element in the compound to moles.
- Divide the number of moles of each element by the smallest number of moles obtained in step 1.
- Simplify the resulting mole ratios to whole numbers (if possible).
Examples of Determining Molecular and Empirical Formulas
Compound:Benzene (actual molar mass: 78 g/mol)
Mass Analysis:92.3% C, 7.7% H
Empirical Formula:CH
Molecular Formula:C 6H 6
3. Using Molecular and Empirical Formulas
Calculating Molar Mass
The molar mass of a compound can be calculated using the molecular formula. Simply add the atomic masses of all the atoms in the formula.
Determining Composition
The molecular or empirical formula can be used to determine the mass percentage of each element in the compound.
Examples of Using Molecular and Empirical Formulas
Compound:Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Molecular Formula:NaCl
Molar Mass:58.44 g/mol
Mass Percentage of Sodium:39.34%
Mass Percentage of Chlorine:60.66%
Popular Questions
What is the difference between a molecular formula and an empirical formula?
A molecular formula represents the exact number of atoms of each element present in a molecule, while an empirical formula provides the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound.
How can I determine the molecular formula of a compound?
To determine the molecular formula, you need to know the empirical formula and the molar mass of the compound.
What are the applications of molecular and empirical formulas?
Molecular and empirical formulas are used in various chemical calculations, including determining molar mass, calculating the composition of compounds, and predicting chemical reactions.