Unveiling the mysteries of the human body’s largest organ, the integumentary system worksheet answers provide an in-depth exploration of the skin, its appendages, and its vital functions. Embark on a journey of discovery as we delve into the protective layers, sensory capabilities, and intricate mechanisms that safeguard and sustain us.
From the outermost epidermis to the underlying layers, the skin serves as a resilient barrier against external threats and plays a pivotal role in regulating body temperature, synthesizing vitamin D, and enabling sensations. Hair, nails, and sweat glands, as extensions of the integumentary system, contribute to thermoregulation, protection, and waste elimination.
1. Integumentary System Overview: The Integumentary System Worksheet Answers
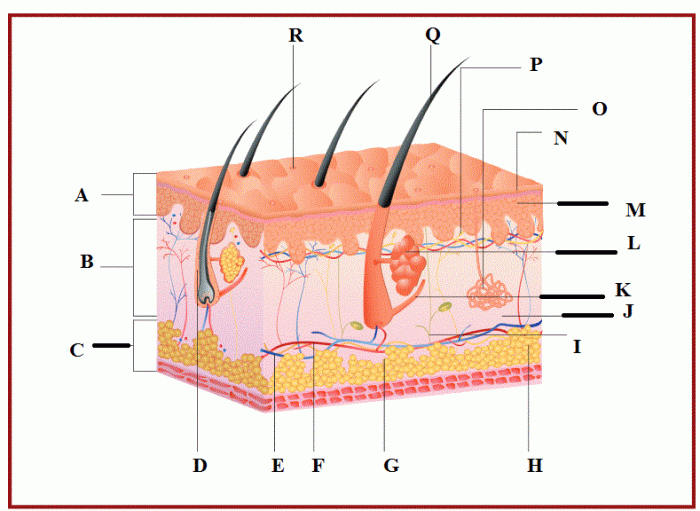
The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body, consisting of the skin, hair, nails, and sweat glands. It serves as a protective barrier, regulates body temperature, and plays a role in sensation, vitamin D synthesis, and waste elimination.The
skin is composed of three main layers: the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The epidermis, the outermost layer, provides a waterproof barrier and contains cells that produce melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. The dermis, the middle layer, provides strength and elasticity to the skin and contains blood vessels, nerves, and hair follicles.
The hypodermis, the innermost layer, consists of fat cells that insulate the body and provide cushioning.
2. Skin Functions
The skin performs numerous essential functions:
-
-*Protection
The skin acts as a physical barrier against pathogens, UV radiation, and chemicals.
-*Thermoregulation
Blood vessels in the skin dilate or constrict to regulate body temperature.
-*Sensation
Nerve endings in the skin allow us to perceive touch, temperature, and pain.
-*Vitamin D synthesis
The skin produces vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, which is essential for bone health.
-*Waste elimination
Sweat glands release water and electrolytes, eliminating waste products from the body.
The skin adapts to different environments: in cold climates, it thickens to provide insulation, while in warm climates, it becomes thinner to enhance heat dissipation.
3. Skin Appendages
Skin appendages include hair, nails, and sweat glands:
-
-*Hair
Hair follicles produce hair, which insulates the body and protects the scalp from UV radiation.
-*Nails
Nails are made of keratin, a hard protein, and protect the fingertips and toes.
-*Sweat glands
Sweat glands secrete sweat to regulate body temperature and eliminate waste products.
4. Skin Disorders, The integumentary system worksheet answers
Common skin disorders include:
-
-*Acne
A skin condition characterized by pimples and blackheads, caused by bacteria and hormonal changes.
-*Eczema
A chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and red skin.
-*Psoriasis
An autoimmune disorder that causes red, scaly patches on the skin.
Causes, symptoms, and treatments vary depending on the disorder.
5. Skin Care and Maintenance
Proper skin care is essential for skin health:
-
-*Cleansing
Regularly cleanse the skin to remove dirt and bacteria.
-*Moisturizing
Apply moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness.
-*Sun protection
Use sunscreen to protect the skin from UV radiation.
-*Healthy diet and lifestyle
A balanced diet and regular exercise contribute to overall skin health.
FAQ Section
What are the key functions of the skin?
The skin provides protection against pathogens, UV radiation, and physical damage. It aids in thermoregulation, sensation, and vitamin D synthesis.
How do hair follicles contribute to thermoregulation?
Hair follicles contain muscles that contract or relax to trap or release heat, aiding in body temperature regulation.
What are some common skin disorders?
Common skin disorders include acne, eczema, and psoriasis, each with distinct causes, symptoms, and treatments.